Loading...
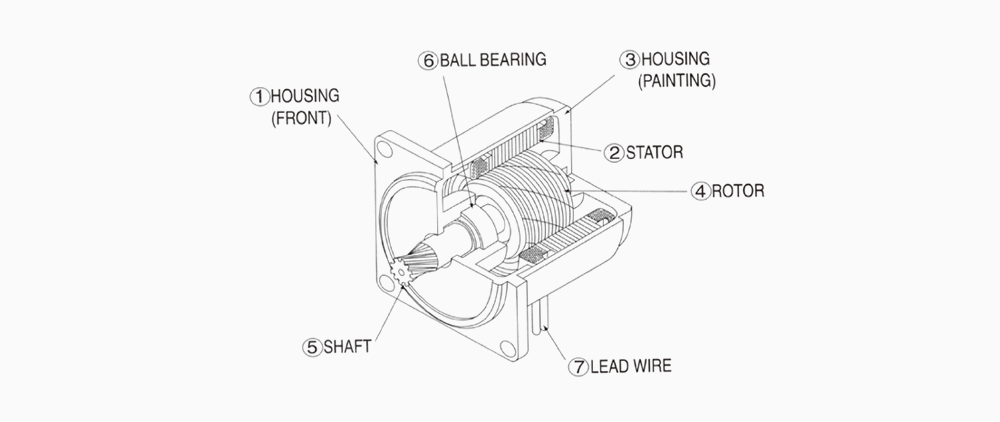
① FLANGE (FRONT)
② STATOR
③ HOUSING(PAINTING)
④ ROTOR
⑤ SHAFT
⑥ BALL BEARING

NOTE)
The single track deep groove ball bearing type is the most typical type among roller bearings, which purpose of use is very extensive, and the groove on the inner and outer ring raceways has a slightly larger curvature radius than the radius of the rolling element (ball). This bearing can take loads in any direction, including radial direction loads, axial loads and combined loadsand, moreover, it has less friction torque,which is most appropriate for the purpose requiring high speed spinning, low noise, and vibration.
This type of bearing includes an open type bearing, shielded or sealed type bearing with a rubber seal and abearing in the form of a snap ring is attached to the outside diameter of the outer ring.
⑦ LEAD WIRE

| IP Indication |
Type of Protection for Dustproof | |
|---|---|---|
| Degree of Protection | Test conditions. | |
| IP0□ | None | None |
| IP1□ | Protection from the hand approaching | Not to be penetrated by foreign object of more than diameter 30mm |
| IP2□ | Protection from the fingers approaching | Not to be penetrated by foreign object of more than diameter 12mm |
| IP3□ | Protection from the tip of the tool etc. | Not to be penetrated by foreign object of more than diameter 2.5mm |
| IP4□ | Protection from the WIRE etc. | Not to be penetrated by foreign object of more than diameter 1.0mm |
| IP5□ | Protection fromdust | Dust will not penetrate that prevents normal operation. |
| IP6□ | Complete Dustproof) Structure | Dust will be fully protected from the infiltration |
| IP Indication |
Type of Protection for Dustproof | |
|---|---|---|
| Degree of Protection | Test conditions | |
| IP□0 | None | None |
| IP□1 | Protection from vertical droplets | Drop of droplet of 3~5 L/min from height of 200mm for 10 minutes |
| IP□2 | Protection from water droplets falling vertically in the range of 15 ° | Drop of droplet of 3~5 L/min from height of 200mm for 10 minutes in range of 15° |
| IP□3 | Protection from water droplets falling vertically in the range of 60 ° | Sprinkle water of 10 L/minute at a height of 200mm for 10 minutes in range of 60° |
| IP□4 | Protection from scattering water in all directions | Sprinkle water of 10 L/minute at a distance of 300 ~ 500mm from all directions for 10 minutes |
| IP□5 | Protection from water to pour from all directions | Pour water of 12.5L/min • 30kPa from a distance of 3m in all directions for 3 minutes |
| IP□6 | Protection from water pouring as like strong waves | Pour water of 100L/min•100kPa from a distance of 3m in all directions for 3 minutes |
| IP□7 | In fixed condition, available to use even sunk in water | For 30 minutes under water |
| IP□8 | Can be used under water | By conference with user and manufacturer side |
Note) All of our CE MARK MOTOR are structured in accordance with the IEC529, IEC34-5 Protection Provisions of the unit, and the IP grade of each MOTOR is set forth in the NAME PLATE.